 2025.08.08
2025.08.08
 Industry News
Industry News
In the fast-paced world of consumer electronics, design is constantly evolving. Nowhere is this more evident than in the smartphone industry, where form and function must coexist seamlessly. As global brands like Apple, Xiaomi, and Samsung push the boundaries of material usage and structural design, the demand for Stamping Mold solutions—especially high-precision molds—has increased significantly.
The Rise of Metal Mid-Frames
In recent years, the metal mid-frame has become the structural core of many smartphones, offering both durability and a premium tactile feel. Unlike plastic or composite materials used in earlier generations, aluminum alloy and stainless steel frames require advanced manufacturing methods. This shift has brought Stamping Mold technology into the spotlight.
Stamping Mold processes are used to shape and cut metal components with micron-level accuracy. For smartphone mid-frames, these molds must deliver high dimensional precision, repeatability, and minimal material waste. Even slight deviations can result in assembly issues, misaligned components, or defects in finish, all unacceptable in premium consumer electronics.
Apple’s Precision Requirements Set the Bar
Apple’s iPhone 15 Pro series, launched in 2023, is a textbook case of how Stamping Mold complexity has escalated. The titanium alloy mid-frame, praised for its strength-to-weight ratio, required custom Stamping Molds capable of handling harder materials without tool wear degradation.
According to a tooling engineer at a key Apple supplier in Shenzhen, “The tolerances for the titanium frame are within ±0.005mm. That’s incredibly tight, and only a few Stamping Mold suppliers worldwide can deliver that level of precision consistently.”
To meet these specifications, mold manufacturers are adopting powder metallurgy tool steels, advanced cooling systems, and precision grinding methods in their Stamping Mold production lines.
Xiaomi and the Push for Thin, Curved Frames
Xiaomi has also contributed to the growing complexity of Stamping Mold needs. The Xiaomi 14 Ultra features a slightly curved, ultra-thin mid-frame that allows for a larger battery without increasing thickness. This type of design demands Stamping Molds that can produce complex 3D shapes while maintaining surface integrity and edge sharpness.
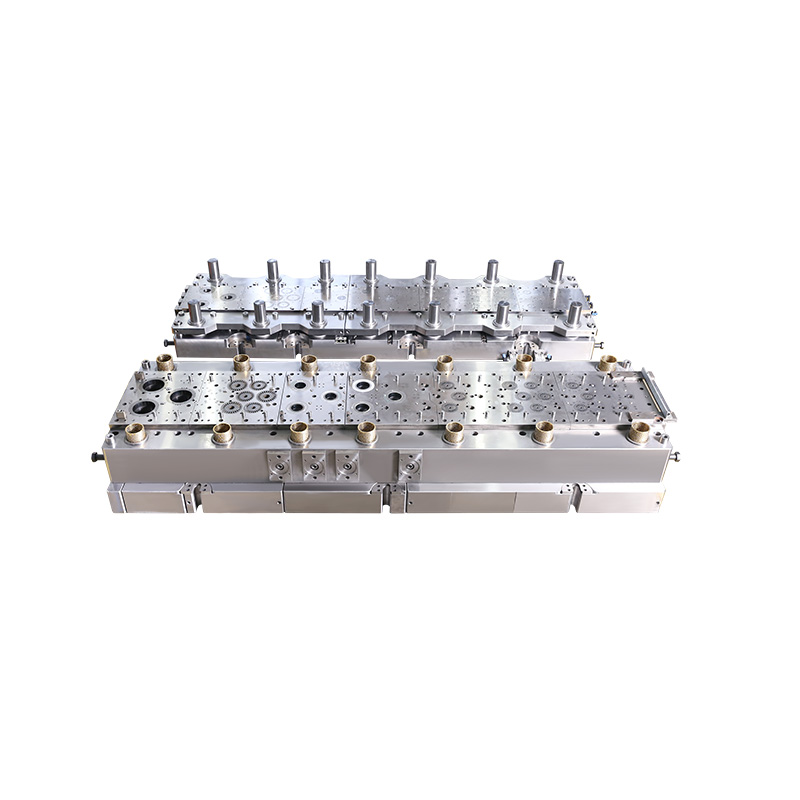

One of Xiaomi’s Tier 1 suppliers, based in Suzhou, shared that they upgraded their Stamping Mold line in early 2024 with real-time wear detection sensors and die-surface polishing automation. “The molds now have to run for 500,000 cycles with minimal wear, or we risk failing to meet delivery schedules,” the company noted.
Tool Life and Cost Efficiency Under Scrutiny
With the production volume of flagship smartphones reaching millions of units per model, Stamping Mold longevity is a critical factor. High-volume production requires molds with long life cycles to reduce downtime and maintenance costs. Suppliers are therefore investing in longer-lasting mold components and advanced coatings like TiCN and DLC (diamond-like carbon) to extend mold life.
Moreover, automation is now playing a larger role in Stamping Mold manufacturing. Mold makers are using CNC and EDM machines integrated with digital twins to simulate real-world performance. This allows for faster iteration and fewer trial runs before mass production.
Looking Forward: Stamping Mold as a Strategic Asset
As smartphones continue to evolve with new materials, thinner bezels, and integrated antenna structures, the importance of precision Stamping Mold solutions will only increase. More than just a tool, the Stamping Mold is becoming a strategic asset in the supply chain of electronics brands.
The global Stamping Mold market for consumer electronics is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% between 2024 and 2028, according to a recent report by Global Tech Insights. Much of this growth will be driven by smartphone innovation.
In the competitive arena of consumer electronics, where product design is a key differentiator, the role of the Stamping Mold has evolved from a backend manufacturing tool to a frontline enabler of innovation. For mold suppliers, staying ahead means mastering not just machining but also materials science, surface technology, and data-driven production.